
Some defects in stack technology are eased in M-LAG, including the three major issues facing stack, as follows: This makes the control plane coupling of M-LAG much looser than that of stack. Unlike stack technology, M-LAG only needs to synchronize information related to interfaces and entries, not all device information. M-LAG technology is essentially a control plane virtualization technology. Therefore, in an M-LAG system, the ports on the two access switches connected to the server are configured as an Eth-Trunk, and MAC addresses and ARP entries of the two ports are synchronized between the two ports.
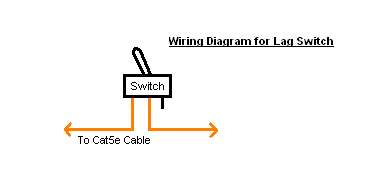
When a server is dual-homed to two access switches, the two NICs on the server use the same MAC address and implement flow-based load balancing. M-LAG also applies to scenarios where a server is dual-homed to two access switches with two NICs working in active-active mode.
M-LAG supports dual-active detection (DAD). In addition, M-LAG supports preferential forwarding of local traffic, minimizing east-to-west traffic between the two switches. In the Layer 3 logical topology, the two switches are two independent devices, can be managed by independent NMSs, and function as independent OSPF nodes. A peer-link is configured between the two switches to exchange M-LAG packets and forward horizontal service traffic between the switches. In Figure 5-3, the two M-LAG switches provide M-LAG interfaces for Layer 2 service access. Figure 5-3 M-LAG-based physical topology and Layer 2 as well as Layer 3 logical topologies


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
